Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that’s found in all cells of the body.
Your body needs some cholesterol to make hormones, vitamin D, and substances that help you digest foods. Your body makes all the cholesterol it needs. However, cholesterol also is found in some of the foods you eat.
Cholesterol travels through your bloodstream in small packages called lipoproteins (lip-o-PRO-teens). These packages are made of fat (lipid) on the inside and proteins on the outside.
Two kinds of lipoproteins carry cholesterol throughout your body: low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL). Having healthy levels of both types of lipoproteins is important.
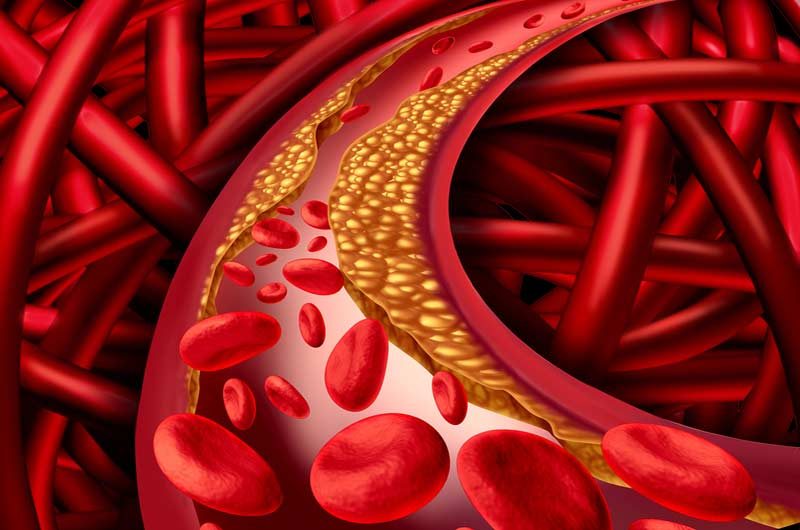
LDL cholesterol sometimes is called “bad” cholesterol. A high LDL level leads to a buildup of cholesterol in your arteries. (Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood from your heart to your body.)
HDL cholesterol sometimes is called “good” cholesterol. This is because it carries cholesterol from other parts of your body back to your liver. Your liver removes the cholesterol from your body.
What Is High Blood Cholesterol?
High blood cholesterol is a condition in which you have too much cholesterol in your blood. By itself, the condition usually has no signs or symptoms. Thus, many people don’t know that their cholesterol levels are too high.
The higher the level of LDL cholesterol in your blood, the GREATER your chance is of getting heart disease. The higher the level of HDL cholesterol in your blood, the LOWER your chance is of getting heart disease.
Lowering your cholesterol may slow, reduce, or even stop the buildup of plaque in your arteries. It also may reduce the risk of plaque rupturing and causing dangerous blood clots.
Making healthy eating choices and increasing exercise are important first steps in improving your cholesterol. For some people, cholesterol-lowering medication may also be needed to reduce the risk for heart attack and stroke.
Source: National Heart Lung and Blood Institute