Many Complications of Diabetes have been known to give rise to other non-related symptoms. That is why you should read this article and get health knowledge that will greatly help you.
Type-2 diabetes is a condition that affects over ¼ of Americans over the age of 65.
Although there has been a dramatic and alarming increase in type-2 diabetes among young people, it has increased at a much faster pace among senior citizens.
According to figures from the National Institutes of Health, By 2050, diabetes among those over the age of 75 will account for 30% of all cases.
Diabetes is also the culprit in many other health complications. Many of these complications like neuropathy, coronary heart disease, and stroke are well known.
Also, much progress has been made on the part of the medical community to mitigate these risks.
But what about lesser-known but serious complications of diabetes encountered by the elderly?
Continue reading for four of these complications and how you and your caregiver can manage them.
4 Major Complications of Diabetes and Management
Hearing loss
Although common among the elderly in general, hearing loss is especially acute among seniors with diabetes. Over time, high glucose levels can lead to damaged blood vessels and nerves in the ear.
Unfortunately, hearing loss cannot be reversed, but properly managing your blood sugar can prevent further damage. Hearing aids will also help.
Vision impairment
Vision impairment is another common symptom of aging that is made worse by diabetes.
High glucose levels affect the eyes much the same way as the ears. Damaged or broken blood vessels can cloud your vision and eventually lead to blindness (e.g. diabetic retinopathy).
Although treatable with laser surgery, the blindness can return if you don’t manage you blood sugar levels. You should also have your A1C glucose levels checked twice a year to try and spot any issues early.
Cognitive impairment
Higher blood sugar levels also increase the risk of dementia according to research published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Other studies have shown increased blood sugar damaging neurons in the brains of animals. Cognitive impairments like dementia can lead a person to not manage their diabetes, which puts them at higher risk.
Family members mustn’t overreact, they should encourage independence and provide support.
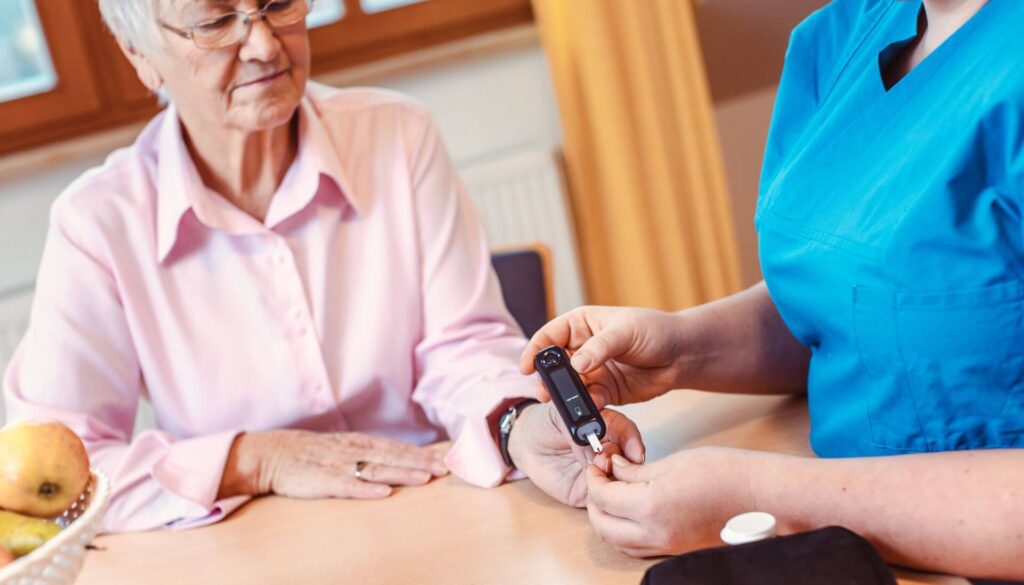

Mobility
Getting around becomes more of a challenge as we age, but diabetes can exacerbate it.
Complications like arthritis and other bone and joint issues are common as we age. Diabetes can also lead to neuropathy or nerve damage in the feet. Loss of feeling in the feet is the main symptom of this condition.
Staying as active as you can helps reduce pain and also boosts blood sugar levels.
Again, type-2 diabetes is getting more common among the aging population. Sharing any concerns with your doctor or caregiver as soon as you notice them will dramatically increase the odds of mitigating these effects.
Waiting too long and not managing the diabetes could eventually lead to blindness, deafness, or chronic pain, which is why managing your health as a diabetic is critical to maintaining an independent lifestyle.
Summary: Complications of Diabetes
Diabetes is a health complication that affects men and women of all age groups. However, this condition is known to be prevalent among the elderly.
It will interest you to know that diabetes can spring up other complications that are diabetes unrelated, such as hearing loss, sight impairment, and mobility complications among others.
Early diagnosis will help curtail these serious health challenges and generally, aging seniors should always undergo routine health checks and maintain a healthy lifestyle.